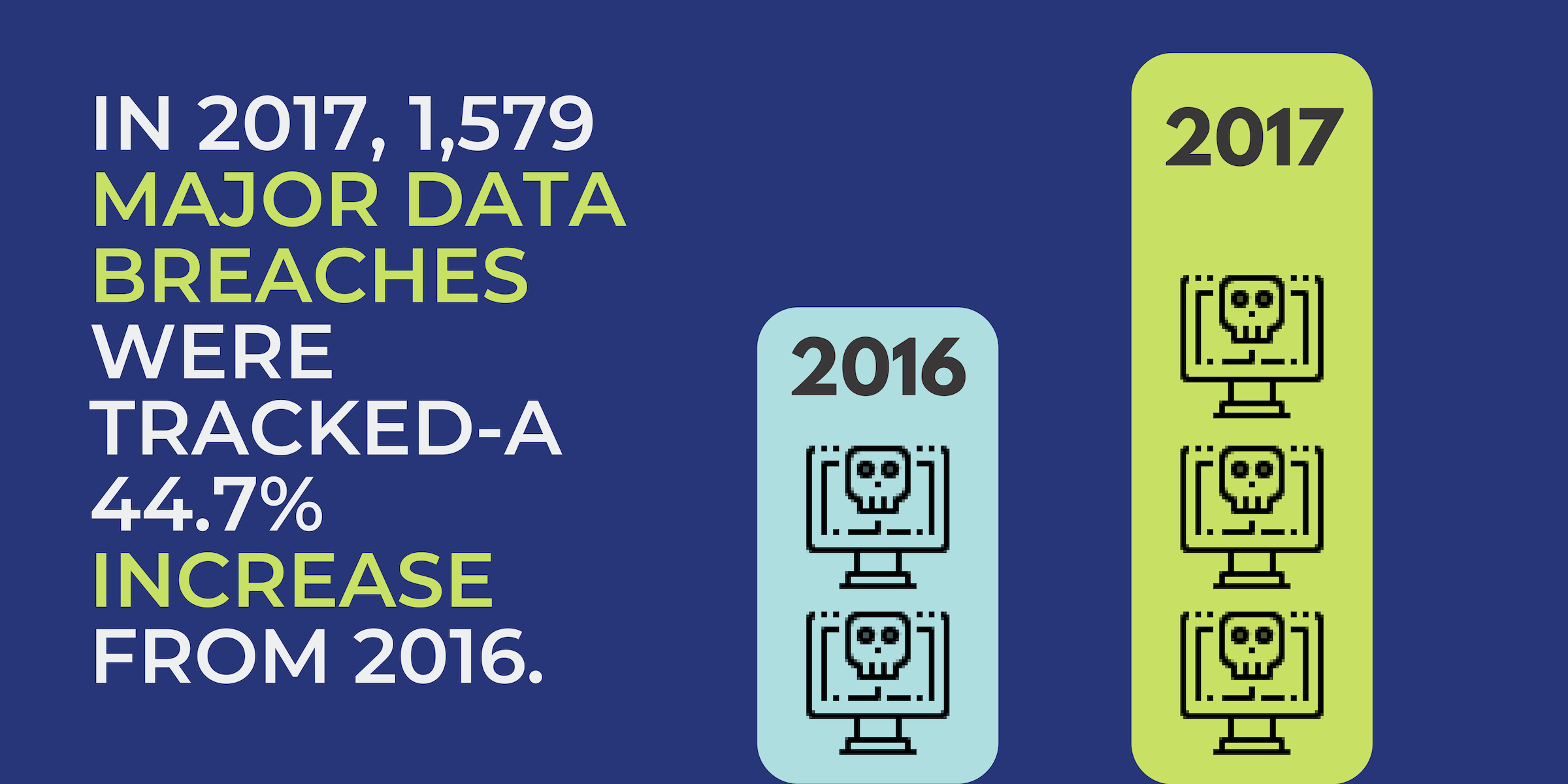
![]() You’ve likely seen some of the massive stats in the news. Nearly a week goes by without a major data breach. But what few in the general public know is that nearly every organization is hacked.
You’ve likely seen some of the massive stats in the news. Nearly a week goes by without a major data breach. But what few in the general public know is that nearly every organization is hacked.
Professional cyber security consultants note that it’s very rare to find an organization whose data is not compromised in some way. In cyber security circles the acronym C.I.A. sums up the major ways in which data can be at risk.
- C: The Confidentiality of data can be comprimised
- I: The Integrity of data can be comprised
- A: The Availability of data can be comprimised
Any three can cause massive fallout to business, particularly those that conduct some of their business online.
Even for small businesses, the average data breach costs over $3.6 million dollars.
If the business risks don’t pique your interest. Perhaps the range of demand for cyber security professionals will. In 2019, over 1 million cyber security jobs went unfilled. A million. And by 2021, an estimated 3.5 million cyber security professional positions will be unfilled in America alone. Talk about a seller’s market. And as with every organizational endeavor, strong leaders and managers are needed to meet organizational goals. That leads us to our primary subject today, master’s in business administration degrees in cyber security.
While there aren’t a huge range of programs offering cyber security-specific MBAs, information technology MBAs have long been a mainstay of graduate business education. Many of these IT MBAs provide courses in cyber security and cyber security management. On top of this, a growing range of programs are offering cyber security-specific curricula.
At MBACentral, we’ve covered all sorts of MBAs and graduate business school topics. If you think you might be interested in a cyber security MBA, be sure to check out some of our resources below, or keep scrolling to read what you can do with a cyber security mba today!
Cyber Security MBA Resources
- The Best Online Cyber Security MBAs
- The Best Online Information Technology MBAs
- The Most Accelerated Online MBAs
- The Best No-GMAT Online MBAs
- The Best Online MBA Programs
What is a Cyber Security MBA?
Cyber security or information assurance MBAs are master’s-level professional degrees. They typically require 1-3 years to finish, depending on whether your program is part-time, full-time, or accelerated.

Master’s in business administration (MBA) degrees are some of the most well-known graduate business degrees. They provide utility, expertise, and experience in a wide range of business, leadership, and managerial roles.
Additionally, MBAs are some of the few degrees that provide academic understanding that aids professionals from lower management through executive positions. A recent survey found that more executives of S&P500 corporations held an MBA than all other forms of graduate degrees combined.
MBAs in cyber security are comprised of two elements:
- Core MBA Courses
- Specialization or Concentration Courses in Cyber Security Topics
Most MBA programs have similar core courses. This collection of courses is meant to provide you with a foundational knowledge of many of the business disciplines you may encounter in your career.
Common core courses within a master’s in business administration program include:
- Marketing
- Strategy
- Financial Accounting
- Corporate Finance
- Statistics for Business
- Economics for Business
- Leadership
- Operations or Supply Chain Management
- Analytics for Business
- Global Business
Students work through the above courses in greater or less depth depending on a number of factors including whether or not one of the above topics is your concentration, whether you’re in a traditional or executive MBA, and whether you’ve transferred any credits into the program.
Concentrations or focus areas within MBAs are commonly available in non-executive MBAs (more on that later). They commonly involve taking 3-5 courses in a given subject area and many specialization programs allow you to tailor your course of study by selecting electives that particularly interest you.

An MBA concentration in cyber security may include courses like the following:
- IT and Cyber Security Technology for Managemers
- Data Warehousing and Security
- Cyber Security law, policy, compliance, and ethics
- Penetration testing, monitoring and auditing in IT
- Global Cyber Scurity
- Management of Information Security Systems
- Human Elements in Cyber Security
- Policy in Cyber Security
- Privacy in Cyber Security
When looking for a cyber security MBA< students should be aware of key differences between traditional MBAs and an executive MBA. Traditional MBAs are often open to students directly out of undergraduate study or with 1-2 years of work experience. They start from a foundational level in graduate business courses, and often take 2-3 years to complete.
Executive MBAs are open to those with 5 or more years of managerial experience. This prerequisite allows programs to assume that those enrolled are familiar with foundational business knowledge in a range of disciplines. This means that executive MBAs often require less course work as well as cover more advanced topics. One other key difference is that executive MBAs often do not offer specializations. For those looking for an MBA in cyber security, this can be a “deal breaker.”
Think you might be interested in a cyber security mba? Check out MBACentral’s ranking of the best online cyber security MBA’s today!
An MBA VS. an MS in Cyber Security
For those looking for a graduate degree related to cyber security, many end up choosing between an MS in Cyber Security and a MBA in Cyber Security.
While both of these degrees can help you to advance in cyber security-related roles, the subjects covered in the following programs are quite different. Below we’ll highlight some of the key differences between MBAs and MS degrees in cyber security.
MBA in Cyber Security Key Facts
- Primarily a graduate business and management degree with a handful of cyber security courses
- Cyber security courses tend to focus on management of technical talent , policy, ethics, and selling of cyber security products
- Can be completed in 2-3 years
- Can prepare students for a wide range of business positions
MS in Cyber Security Key Facts
- Primarily an information technology and engineering degree with a handful of management courses
- Cyber security courses tend to focus on technical aspects of cyber security
- Can be completed in 1-2 years
- Can prepare students for a wide range of cyber security positions and a handful of management positions
While there are a number of roles which are held by both MS in cyber security and cyber security MBA recipients, generally the focus points of the degrees are different. MS programs are much more technical, while MBAs are much more focused on business and management.
One thing to keep, in mind is that many cyber security organizations have a wide range of roles, from director of compliance or security, to ethical hackers. You can’t go wrong with either of the degrees we’re discussing here. But you should likely choose one of the other that more closely aligns with your eventual career goals and current skill disposition.
Think you might be interested in a cyber security mba? Check out MBACentral’s ranking of the best online cyber security MBA’s today!
Can You Get a Cyber Security MBA Online?

While many potential students know there are more online degrees than ever, many looking for an MBA have never taken online courses. That leads many students to question whether MBAs in cyber security are offered online.
The short answer is yes, a large percentage of MBAs with concentrations in cyber security are offered both online and in-person.
There are many benefits to online degrees. With that said, they aren’t for everyone, and each student should carefully weigh the pros and cons of an online and in-person degree as they relate to their own situation.
Some of the most commonly cited positive elements of taking courses or entire degrees online include the following:
- Lower fees than in-person programs
- No need to move, commute, or change jobs
- The same degree from the comfort of wherever you would like to study
- Many programs offer asychronous courses that can be ‘attended’ at any point
- Access to many of the same support services as in-person programs
Meanwhile, some students have trouble with online programs. Some of the most commonly cited negative elements of taking courses or entire degrees online include the following:
- Lack of access to on-campus events
- Harder to ‘get to know’ classmates and professors
- Often requires more of a self-starter mentality
- Not as much of a ‘B-School Experience’
Of the troubles some students have when pursuing an online degree, the most serious cited is often the ‘self-starter’ mentality required of students studying online. With online coursework, there is no one ‘looking over your shoulder’ to ensure that you’re finishing work on time. This is most often the case with asynchronous online coursework without many set “due dates” and in self-paced programs.
Think you might be interested in a cyber security mba? Check out MBACentral’s ranking of the best online cyber security MBA’s today!
What Can You Do With a Cyber Security MBA?
Cyber security MBAs do not guarantee one specific job within a cybersecurity organization. Rather, they provide the academic bedrock for students to ‘bridge the gap’ between managerial concerns, business disciplines, and cyber security.
As cyber security grows in importance in many organizations, professionals that understand how cyber security objectives interface with broader organizational goals will be increasingly important. Roles that require both cyber security and business acumen largely fall into three groups:
- General management of information technology and cyber security teams
- Auditing and Analysis Roles
- Senior cyber security policy advisor roles
Information Technology and Cyber Security Management

By far the most common management role within information technology teams or organizations is that of project manager. Project managers are uniquely suited to the small and fast-moving teams within information technology fields.
Generally speaking, project managers within information technology disciplines are skilled in agile development methodology. Though there are many variations, this management style involves the following:
- Gathering information for a minimum viable product
- Releasing a minimum viable product
- Testing the minimum viable product, noting what ‘breaks’
- Incrementally improving the product by restarting the process
Project managers perform much the same role in the provisioning of information security services or products. Similarly to project managers within other technical disciplines, one of the most sought after skill sets of project managers includes understanding the technical matters the team is tackling as well as having the ability to interface with non-technical stakeholders.
Other in-demand skills for project managers include the following:
- The ability to form a coherent team
- The ability to hire and fire team members
- The ability to mitigate conflict between team members
- The ability to create methods of tracking key performance indicators
- The ability to interface with a variety of stakeholders in the organization
- The ability to understand the technical issues being addressed by team workers
- Solid understanding of agile development methods (or related)
- Ability to perform financial analysis of team actions and outcomes
As you may have guessed, highly qualified project managers are hard to come by, and when they are found are well compensated.
The average salary of information systems-related project managers nationwide is presently $139,220 with a 12% increase in expected job openings over the next 7 years.
Similarly to project managers, program managers help to interface between corporate decision makers, financial departments of an organization, and day-to-day logistics of creating a product or service. Generally programs are comprised of several projects, with program managers often over 20 to several hundred employees.
While many elements related to project management also apply to program management, program managers are also responsible for creating new projects and ensuring that the outcomes of seperate projects work well together.
Common responsibilities of program managers may include:
- Developing a budget split between a number of projects
- Crafting of long-term goals for a program within an organization
- Ensuring tracking methods are in place for project and program success
- Writing program funding proposals
- Analysis of program risks
- Meeting with a variety of stakeholders including lower level technical workers within projects
Program managers often report directly to executives within an organization and depending on the size of an organization may be in charge of budgets of many million dollars. The average salary for program managers is $121,669 a year, though can rise much higher depending on the organization.

Auditing and Analysis Roles
While a more common path for masters in business adminstration recipients without a great deal of experience is to enter into business analyst roles, some MBA grads with cyber security experience may enter roles as security analysts.
Similarly to business analysts, security analysts help to perform original research and produce reports for decision makers within an organization. In particular, security analysts look at technical matters related to cybersecurity. Security analysts are some of the most technical positions one may expect to see MBA graduates in, and few MBA programs will provide graduates with enough technical knowledge to enter these roles on their own. Rather, students who have already worked in information technology or cyber security may find MBA programs a good fit to augment their skills as security analysts are cyber security roles that interface with broader business objectives.
Common tasks of security analysts include researching and implementing cyber security changes both related to technical matters and policy. Additionally, security analysts may be called in in a consultative role to provide their professional opinion about a branch of an organization. Finally, security analysts look at how cyber security risks and implementations affect broader organizational objectives. The ability to interface with a wide range of stakeholders both technical and not is a must for skilled security analysts.
The average salary for security analysts is presently $70,096, with more senior holders of this position making more.
A second auditing and analysis role within cyber security organizations is that of security auditor. Security auditors are mid-level roles responsible for planning security audits across an organization as well as reporting on the financial, privacy-related, and other outcome-based scenarios related to organizational success.
One of the central business functions of security auditors is the creation of the security business continuity and disaster recovery plans. Additionally, security auditors must interface with a wide range of business partners on a wide variety of topics. As areas of expertise MBA programs provide expertise in, security auditors are one of two fairly technical cyber security positions that can benefit most directly from MBAs.
The average salary of security auditors is presently $90,497, with high demand that is only expected to grow.
Senior Cyber Security Policy Advisor Roles
Among cyber security roles, senior policy and advising positions benefit the most directly from MBA degrees. Common cyber security roles functioning at this level of organizations include director of privacy, director of compliance, and chief information security officer (CISO) positions.
As data breaches have become a regular occurrence in American consumers’ lives, privacy matters have become a much more pressing liability for large organizations. In response, director of privacy positions have begun cropping up in many organizations.
Director of privacy positions lie at the heart of cyber security policies, consumers, regulatory bodies, and corporate objectives. These high-level policy positions benefit a great deal from a range of courses in MBA courses of study.
Common responsibilities of director of privacy roles include
- Building comprehensive privacy policies and programs
- Establish relationships and perform negotations between multiple parties regarding privacy
- Oversee risk assessments and inform technical team members of objectives in shoring up risks
- Working on multi-displinary teams including legal counsel, marketing, communications, public relations, management, technical, and customer support
Director of privacy positions generally report directly to chief information security officers (or, if an organization does not have this role), the chief executive officer.
This senior-level position makes an average salary of $147,000, and demand for this at one time seldom seen role is growing.
As cyber security breaches have become more commonplace, regulatory bodies have swept in to monitor and enforce codes of conduct among the once free-for-all scene of consumer data-housing organizations.
With the rise of regulatory risks, the role of director of compliance has risen to prominence in relation to cyber security.
Director of compliance roles are senior-level cyber security roles that often report to chief information security officer or chief executive officer positions. These roles benefit greatly from seasoned professionals well-versed in risk analysis, regulatory matters, public messaging, and negotiations. As such, MBA candidates who properly tailor their courses of study to address some of these components are in a great position for assuming these roles.
Common responsibilities of director of compliance positions include:
- Keeping up with regulations that could be or are applied to your organization
- Blending legal, regulatory, and technical knowledge to understand the impact of regulations
- Negotiating with regulatory bodies, and acting as a liaison between regulatory bodies and organizational stakeholders
- Educating team members company-wide about regulations
While regulatory issues have long been a part of many other industries, information systems and technology organizations are more recently affected. With the threat of fines, lawsuits, and even the shuttering of businesses that can’t keep up with new regulations, director of compliance positions are crucial in many settings.
As one may expect, pay is good for director of compliance positions, with an average salary of over $170,000 a year. The number of job openings for this role are also growing year on year.

One final senior role in cyber security that an MBA can help to prepare you for is that of chief information security officer (CISO). Long part of the chief technology officer role, the recent growth in the seriousness of cyber threats has led to the proliferation of CISO roles across many industries.
Chief information security officers are “c-suite”-level executives who often report directly to the chief executive officer of organizations. CISO’s provide the final say on what direction cyber security initiatives should take in an organization. At a high level, they look at funding needs, key performance indicators, long-term planning, risk assessment, and organization-wide initiatives in cyber security.
While chief information security officers need working knowledge of a wide range of cyber security techniques, tools, and tactics, they are in-the-end overseeing these processes from a strategic level. This makes CISO positions a great role even for those without a massive level of technical knowledge in cyber security.
Cyber security programs that may be overseen by CISO positions include:
- Regulatory compliance
- Ethical Hacking
- Security Audits
- Infrastructure updates and planning
- Educational efforts
- Creation of new products
- And more
As one may expect, CISO positions are well compensated, with an average salary of over $200,000 a year. In some competitive markets, CISO’s make over $400,000 a year.
Think you might be interested in a cyber security mba? Check out MBACentral’s ranking of the best online cyber security MBA’s today!